
What kind of chair is ergonomic?
Publish Time: 2024-09-09
Nowadays, more and more people have to sit in front of the computer for more than eight or nine hours a day. When you are a little older and have worked for five or six years, your waist and neck will start to have problems. Many people don't realize a very serious problem, that is: the human body structure is not suitable for sitting, so long-term sitting will cause various problems, such as lumbar spondylosis, cervical spondylosis, hemorrhoids, etc.Ergonomic chairs are specially designed for long-term sitting and can keep you in a good sitting posture as much as possible. The biggest key to ergonomic chairs is that there are many adjustment options, which allow you to find a more comfortable and correct posture. What kind of chair is ergonomic?There is no national mandatory standard for the concept of ergonomics. The design of each product is different, and the explanation is also different. However, the occupational safety and health departments in many regions have some suggestions for chairs. The details are slightly different, but in general, a good chair must meet two points:
What kind of chair is ergonomic?There is no national mandatory standard for the concept of ergonomics. The design of each product is different, and the explanation is also different. However, the occupational safety and health departments in many regions have some suggestions for chairs. The details are slightly different, but in general, a good chair must meet two points: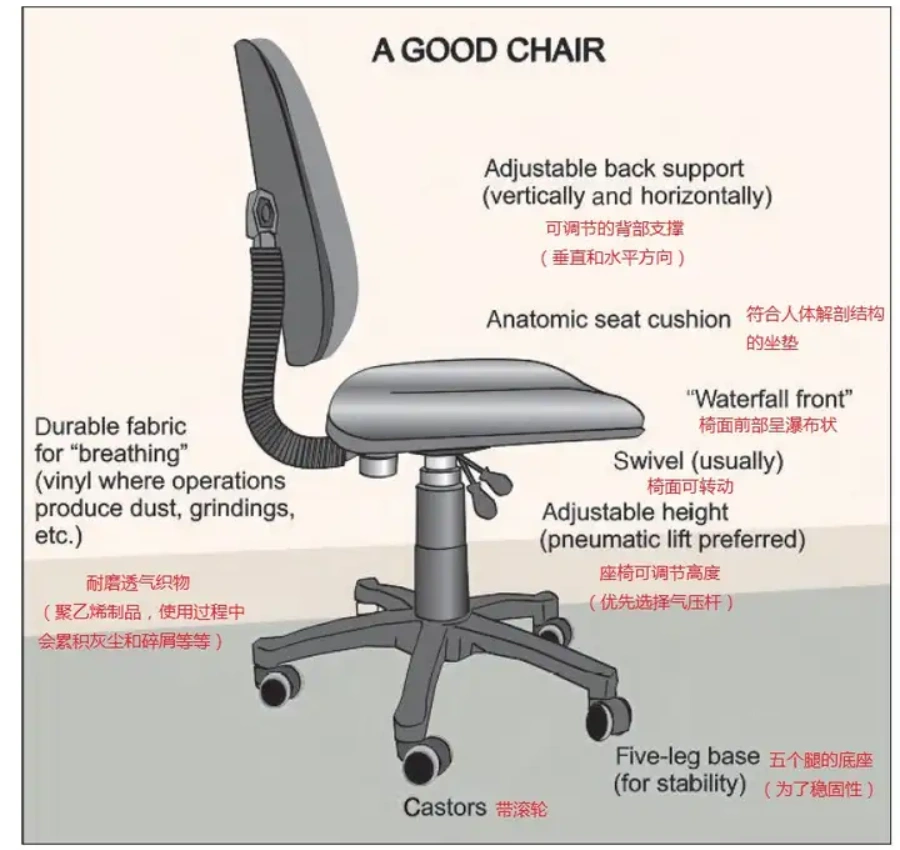 Good lumbar and back support:Fit the spinal curve: The human spine is S-shaped when viewed from the side. The backrest of an ergonomic chair should be able to fit the back and lumbar spine curve of the human body closely, provide sufficient support for the lumbar spine and back, maintain the natural shape of the spine, and reduce spinal deformation and fatigue caused by long-term sitting. For example, the backrests of some chairs are designed to have an arc shape and can be adjusted according to the needs of the user to better adapt to the body shape and sitting habits of different people.Adjustable lumbar support: The lumbar support is a key part of providing lumbar support. An ideal ergonomic chair should have an adjustable lumbar support that can be adjusted up and down, left and right, or forward and backward, so that users can make precise adjustments according to their waist position and needs, ensuring that the waist is always strongly supported and relieves waist pressure.Comfortable seat surface:Appropriate size: The depth and width of the seat surface should be suitable for the user's body shape. The depth of the seat should ensure that the thighs of the user can be fully supported when sitting down, and the legs will not be compressed due to the seat being too deep, affecting blood circulation; the width of the seat should allow the user's buttocks to sit comfortably on the chair and have a certain amount of space for movement. Generally speaking, for adults, the seat depth is 40-45 cm and the width is 40-50 cm.Excellent material:Good breathability: It is easy to sweat when sitting on a chair for a long time, so the seat material needs to have good breathability. Common mesh material is a better choice. It has good elasticity and breathability, which can allow air circulation and reduce the feeling of stuffiness and humidity; although the sponge seat is soft, it has relatively poor breathability and is suitable for people who have high requirements for softness and relatively short use time; and the leather seat, although it looks textured, has poor breathability and is easy to get stuffy in summer, but it is easy to clean and maintain.Good support: The seat material should have sufficient support to withstand the weight of the user and avoid collapse after long-term use. High-resilience sponges or high-quality mesh fabrics perform better in terms of support and can provide stable support for users.Adjustable seat inclination: The seat inclination should preferably be adjustable. Generally speaking, the forward inclination angle can be between 0-5 degrees and the backward inclination angle can be between 0-15 degrees, so that users can adjust it according to their work needs and comfort level. For example, when doing work that requires the body to lean forward, such as writing or operating a computer, the seat can be tilted slightly forward; when resting or relaxing, the seat can be tilted backward to reduce the pressure on the waist and legs.Suitable headrest:Adjustable height: The height of the headrest should be able to be adjusted according to the user's height and sitting posture to ensure that the head can be effectively supported at all times. For taller people, the headrest needs to be adjusted higher; for shorter people, the headrest should be adjusted lower. Generally speaking, the adjustment range of the headrest should meet the needs of most people, for example, it can be adjusted up and down by about 10-15 cm.Adjustable angle: The angle of the headrest should also be adjustable so that the user can rest his head on the headrest in different sitting positions and maintain the natural curvature of the cervical spine. For example, when the user leans back on the chair to rest, the headrest can be adjusted to a suitable angle to provide support for the neck and relieve neck fatigue.Reliable armrests:Height adjustment: The height of the armrest should match the height of the seat and the tabletop, allowing the user's arms to rest naturally on the armrests to reduce shoulder and arm fatigue. The height adjustment range of the armrest is generally between 15-25 cm, which can adapt to users of different heights and tabletops of different heights.Appropriate width: The width of the armrest should be moderate, neither too narrow to cause the arm to be insufficiently supported, nor too wide to affect the user's entry and exit of the chair. Generally speaking, the width of the armrest is more appropriate between 5-10 cm.Adjustable angle: The angle of the armrest should also be adjustable so that the user can maintain a comfortable position with his arms in different sitting positions. For example, when typing or using a mouse, the armrest can be adjusted to an angle parallel to the desktop to facilitate arm operation; when resting, the armrest can be adjusted to a slightly upward angle to relax the arm.Stable chassis and tripod:Chassis: The chassis is the supporting structure of the chair and should have sufficient stability and strength to withstand the user's weight and the pressure generated by various movements. High-quality chassis are usually made of high-strength steel or aluminum alloy materials, and are strictly tested and certified to ensure their safety and reliability.Tripod: The material and structure of the tripod also need to have sufficient stability. Generally speaking, the five-claw tripod is a more common design, which can evenly distribute the weight of the chair and ensure that the chair will not shake or tilt during use. The wheels of the tripod should have good wear resistance and sliding properties, so that users can move freely in the workplace and stay in place stably when stationary.Adjustable chair back tilt function: The chair back tilt angle should be adjustable and can be locked at different angles to meet the different needs of users when working and resting. For example, when working, the chair back can be kept at a relatively upright angle to help users maintain a good sitting and working posture; when resting, the chair back can be tilted back to allow users to relax and relieve fatigue. At the same time, the tilting force of the chair back should also be adjustable so that users of different weights can easily adjust the angle of the chair back.
Good lumbar and back support:Fit the spinal curve: The human spine is S-shaped when viewed from the side. The backrest of an ergonomic chair should be able to fit the back and lumbar spine curve of the human body closely, provide sufficient support for the lumbar spine and back, maintain the natural shape of the spine, and reduce spinal deformation and fatigue caused by long-term sitting. For example, the backrests of some chairs are designed to have an arc shape and can be adjusted according to the needs of the user to better adapt to the body shape and sitting habits of different people.Adjustable lumbar support: The lumbar support is a key part of providing lumbar support. An ideal ergonomic chair should have an adjustable lumbar support that can be adjusted up and down, left and right, or forward and backward, so that users can make precise adjustments according to their waist position and needs, ensuring that the waist is always strongly supported and relieves waist pressure.Comfortable seat surface:Appropriate size: The depth and width of the seat surface should be suitable for the user's body shape. The depth of the seat should ensure that the thighs of the user can be fully supported when sitting down, and the legs will not be compressed due to the seat being too deep, affecting blood circulation; the width of the seat should allow the user's buttocks to sit comfortably on the chair and have a certain amount of space for movement. Generally speaking, for adults, the seat depth is 40-45 cm and the width is 40-50 cm.Excellent material:Good breathability: It is easy to sweat when sitting on a chair for a long time, so the seat material needs to have good breathability. Common mesh material is a better choice. It has good elasticity and breathability, which can allow air circulation and reduce the feeling of stuffiness and humidity; although the sponge seat is soft, it has relatively poor breathability and is suitable for people who have high requirements for softness and relatively short use time; and the leather seat, although it looks textured, has poor breathability and is easy to get stuffy in summer, but it is easy to clean and maintain.Good support: The seat material should have sufficient support to withstand the weight of the user and avoid collapse after long-term use. High-resilience sponges or high-quality mesh fabrics perform better in terms of support and can provide stable support for users.Adjustable seat inclination: The seat inclination should preferably be adjustable. Generally speaking, the forward inclination angle can be between 0-5 degrees and the backward inclination angle can be between 0-15 degrees, so that users can adjust it according to their work needs and comfort level. For example, when doing work that requires the body to lean forward, such as writing or operating a computer, the seat can be tilted slightly forward; when resting or relaxing, the seat can be tilted backward to reduce the pressure on the waist and legs.Suitable headrest:Adjustable height: The height of the headrest should be able to be adjusted according to the user's height and sitting posture to ensure that the head can be effectively supported at all times. For taller people, the headrest needs to be adjusted higher; for shorter people, the headrest should be adjusted lower. Generally speaking, the adjustment range of the headrest should meet the needs of most people, for example, it can be adjusted up and down by about 10-15 cm.Adjustable angle: The angle of the headrest should also be adjustable so that the user can rest his head on the headrest in different sitting positions and maintain the natural curvature of the cervical spine. For example, when the user leans back on the chair to rest, the headrest can be adjusted to a suitable angle to provide support for the neck and relieve neck fatigue.Reliable armrests:Height adjustment: The height of the armrest should match the height of the seat and the tabletop, allowing the user's arms to rest naturally on the armrests to reduce shoulder and arm fatigue. The height adjustment range of the armrest is generally between 15-25 cm, which can adapt to users of different heights and tabletops of different heights.Appropriate width: The width of the armrest should be moderate, neither too narrow to cause the arm to be insufficiently supported, nor too wide to affect the user's entry and exit of the chair. Generally speaking, the width of the armrest is more appropriate between 5-10 cm.Adjustable angle: The angle of the armrest should also be adjustable so that the user can maintain a comfortable position with his arms in different sitting positions. For example, when typing or using a mouse, the armrest can be adjusted to an angle parallel to the desktop to facilitate arm operation; when resting, the armrest can be adjusted to a slightly upward angle to relax the arm.Stable chassis and tripod:Chassis: The chassis is the supporting structure of the chair and should have sufficient stability and strength to withstand the user's weight and the pressure generated by various movements. High-quality chassis are usually made of high-strength steel or aluminum alloy materials, and are strictly tested and certified to ensure their safety and reliability.Tripod: The material and structure of the tripod also need to have sufficient stability. Generally speaking, the five-claw tripod is a more common design, which can evenly distribute the weight of the chair and ensure that the chair will not shake or tilt during use. The wheels of the tripod should have good wear resistance and sliding properties, so that users can move freely in the workplace and stay in place stably when stationary.Adjustable chair back tilt function: The chair back tilt angle should be adjustable and can be locked at different angles to meet the different needs of users when working and resting. For example, when working, the chair back can be kept at a relatively upright angle to help users maintain a good sitting and working posture; when resting, the chair back can be tilted back to allow users to relax and relieve fatigue. At the same time, the tilting force of the chair back should also be adjustable so that users of different weights can easily adjust the angle of the chair back.


